Selective Catalytic ReductionSCR Technology
What is Selective Catalytic Reduction?
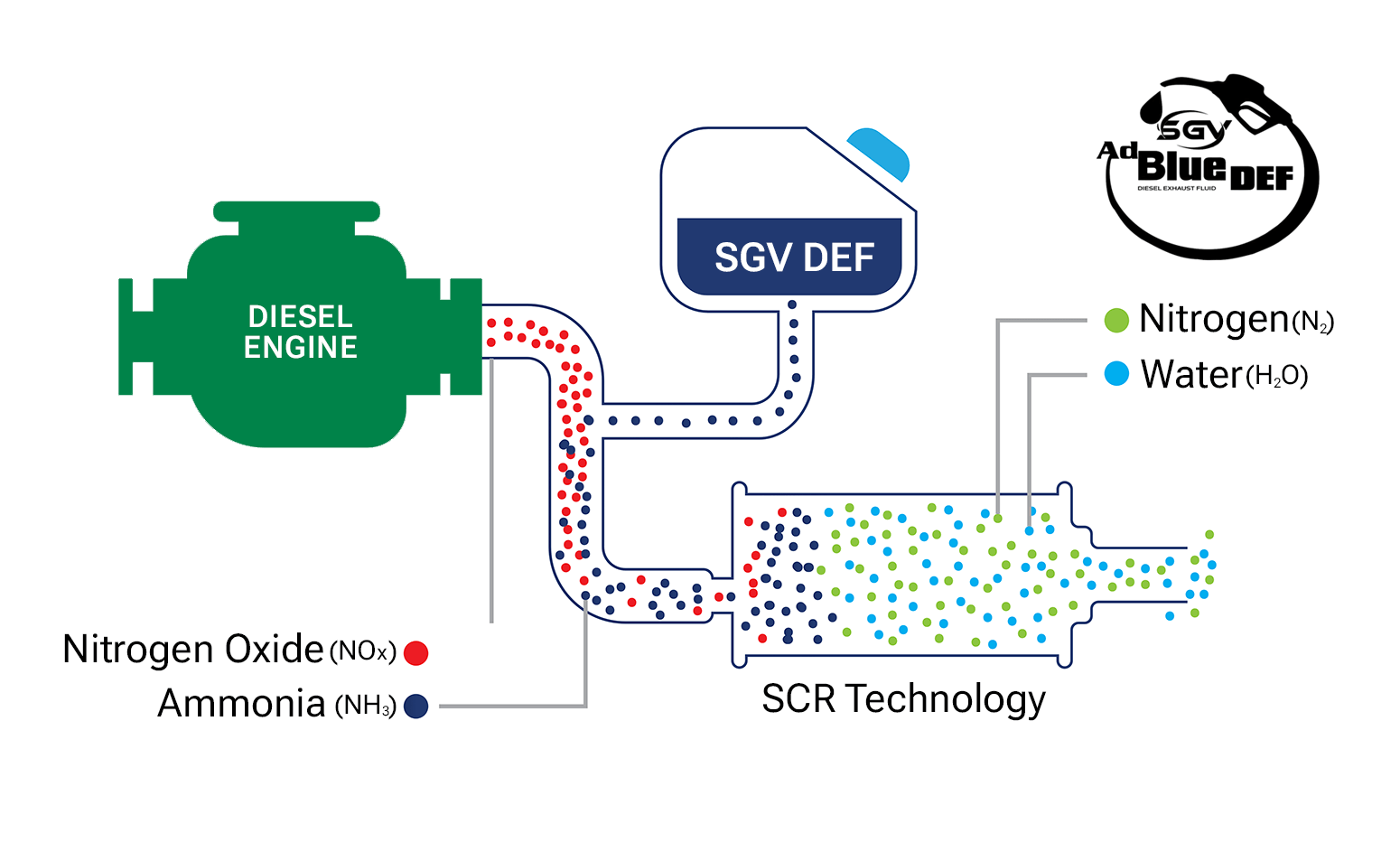
Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) stands as an advanced emissions control technology system actively employed to substantially decrease nitrogen oxides (NOx) emissions to nearly zero levels in modern diesel-powered vehicles and equipment. The SCR system comprises various components integrated with other elements of the emissions control system. Manufacturers may introduce their unique variations in the type and sequencing of these components within the system.
How does Selective Catalytic Reduction work?
SCR operates as an active emissions control system, managing hot exhaust gases from the engine. Within the SCR system, aqueous urea, commonly known as Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF), is sprayed onto a specialized catalyst. This initiates a chemical reaction in the exhaust, converting nitrogen oxides into nitrogen, water, and minimal amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2) – components naturally present in the air we breathe. The exhaust then traverses a particulate filter within the system before being expelled through the vehicle tailpipe.
The unique design of SCR technology facilitates nitrogen oxide (NOx) reduction reactions in an oxidizing atmosphere. Termed "selective," this process diminishes NOx levels by utilizing ammonia as a reductant within a catalyst system. This reduction reaction involves DEF as the reducing agent, transforming NOx pollutants into nitrogen, water, and slight amounts of CO2. The DEF undergoes rapid breakdown, generating oxidizing ammonia within the exhaust stream.
Why SCR is important?
SCR technology stands as one of the most cost-effective and fuel-efficient solutions, effectively contributing to the near elimination of emissions from diesel engines. Since 2011, all heavy-duty diesel truck engines have incorporated SCR technology to meet the latest EPA emissions standards.
These stringent standards mandate a significant reduction in particulate matter (PM) and nitrogen oxides (NOx), aiming for near-zero levels. SCR proves highly effective, capable of reducing NOx emissions by up to 90%, while simultaneously cutting down HC and CO emissions by 50-90% and PM emissions by 30-50%. When coupled with a diesel particulate filter, SCR systems can achieve even more substantial reductions in PM emissions.
The remarkable efficiency of SCR systems in reducing NOx emissions enables manufacturers to strike a balance between engine performance, maximum fuel economy, and the attainment of near-zero emissions. Some operators of heavy-duty commercial trucks equipped with SCR report fuel economy gains exceeding 4%.
Why SCR is used?
For decades, SCR has served as a fundamental control strategy in mitigating emissions from stationary industrial sources. Beyond its application in on-highway commercial trucks, SCR systems are employed in various off-road engines and equipment utilized in construction, farming, marine, rail, and power generation. These systems play a crucial role in meeting latest emissions standards, necessitating comparable reductions in NOx, PM, and other pollutants as observed in on-highway vehicles. Recognizing its notable economic and environmental advantages, SCR technology is increasingly incorporated into diesel-powered pick-up trucks, vans, and SUVs.

